41 plastids diagram with labels
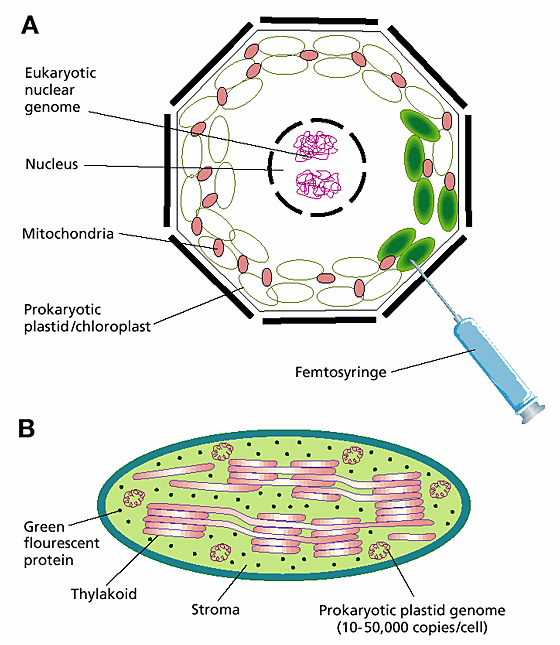
Chloroplasts and Other Plastids - The Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for photosynthesis, are in many respects similar to mitochondria. Both chloroplasts and mitochondria function to generate metabolic energy, evolved by endosymbiosis, contain their own genetic systems, and replicate by division. However, chloroplasts are larger and more complex than mitochondria, and they perform several critical tasks in addition to the ... Plastids - Types and Structure - VEDANTU The double membrane organelles found in the cells of plants and algae are called plastids. They are also found in some eukaryotic organisms. They are of endosymbiotic origin. The main function of plastids is to manufacture and store food.
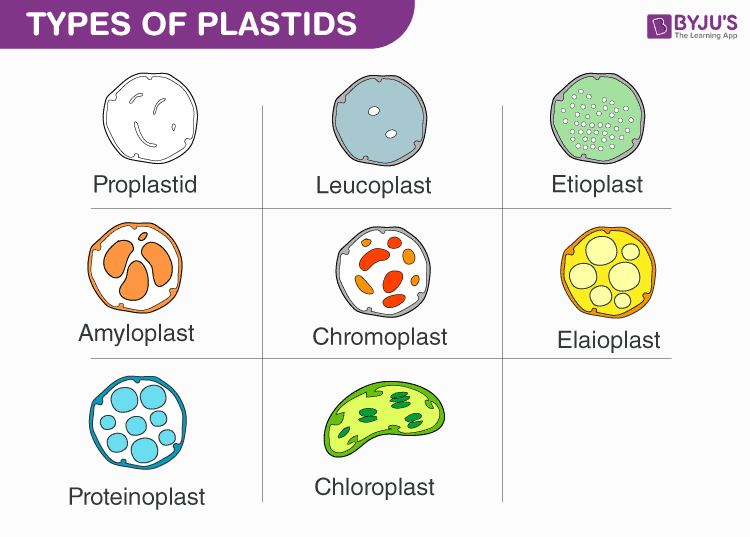
Plastids: Types, Structure and Function (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Plastids may be coloured or colourless and are of three types. The leucoplasts are the colourless plastids principally serving the purpose of storage. On the basis of nature of storage compound, leucoplastids are amyloplasts (starch), elaioplasts (oil) or aleuroplasts (protein). The green plastids or chloroplastids are needed for photosynthesis.
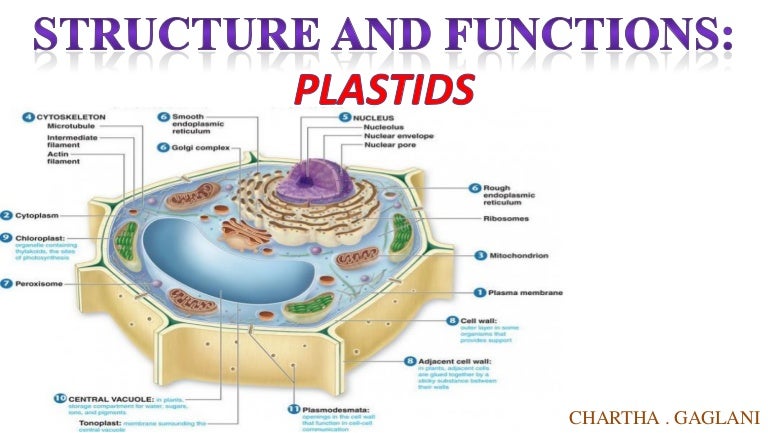
Plastids diagram with labels
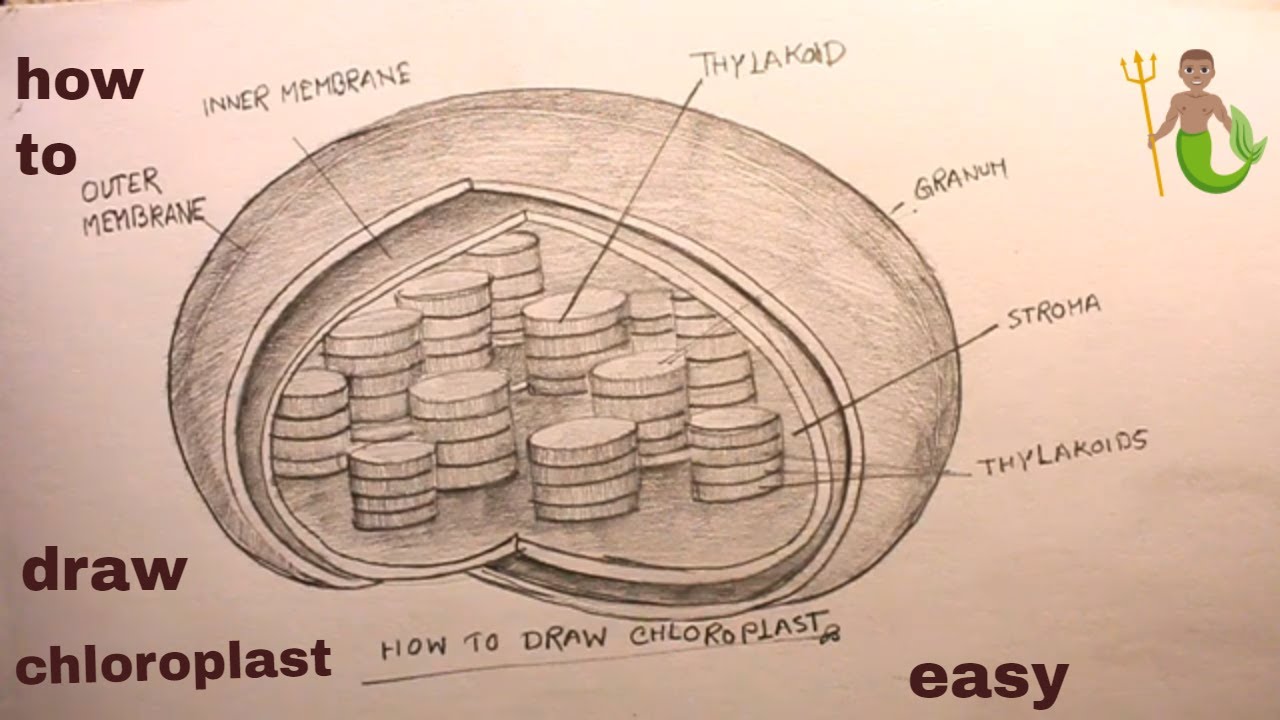
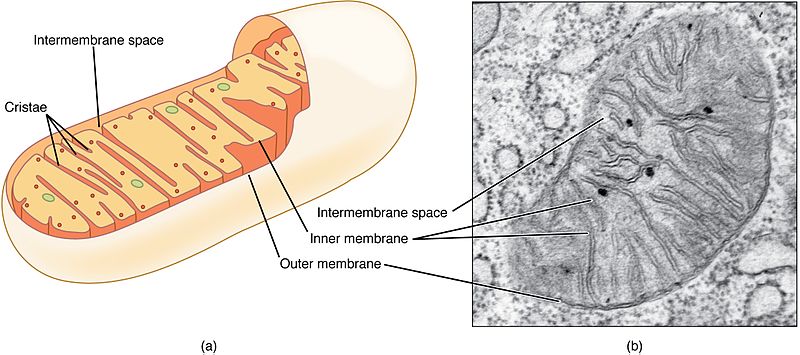
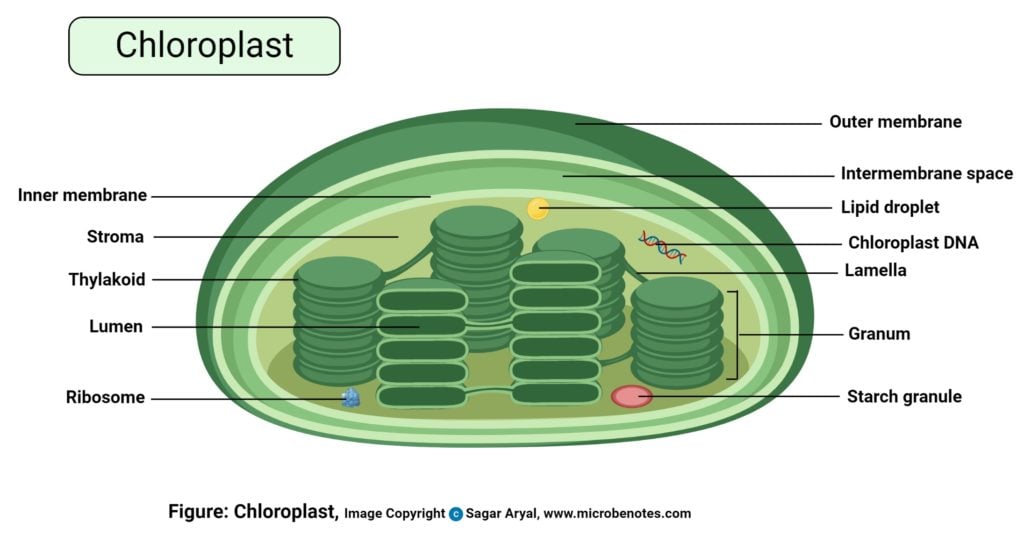
Animal Cells Label The Organelles In The Diagram Below : Plant and ... They include the cell wall, large central vacuole, and plastids 19. As observed in the labeled animal cell diagram, the cell membrane forms the confining factor of the cell, that is it envelopes the cell ribosomes are small, spherical organelles comprising 65% ribosomal rna and 35% ribosomal proteins. Organelles in an animal cell. Plant Cell: Diagram, Types and Functions - Embibe Exams Plastids in Plant Cell, They are membrane-bound organelles that have their own DNA. They are necessary to store starch, to carry out the process of photosynthesis. It is also used in the synthesis of many molecules, which form the building blocks of the cell. Based on the type of pigment, they are of Plastids are of three types: a. Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast - BYJUS The chloroplast diagram below represents the chloroplast structure mentioning the different parts of the chloroplast. The parts of a chloroplast such as the inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane space, thylakoid membrane, stroma and lamella can be clearly marked out. Chloroplast Diagram representing Chloroplast Structure,
Plastids diagram with labels. Plastids: Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram Plastids are double-membrane organelles that contain pigments that are helpful in the process of Photosynthesis and govern the change in the colours of the cells. Plastids also act as storage devices for starch and help in the synthesis of various molecules like fatty acids and terpene. They are found in plants and algae and are responsible for ... Plant Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure - Research Tweet Plant Cells Labelled, Plastids and Chloroplasts, Plants make their own food through photosynthesis. Plant cells have plastids, which animal cells don't. Plastids are organelles used to make and store needed compounds. Chloroplasts are the most important of plastids. They convert light energy from the sun into sugar and oxygen. Study Notes on Genetics of Plastids (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The below mentioned article provides a study note on Genetics of Plastids. In the cytoplasm of the plant cells are found many small cytoplasmic bodies, called plastids. These plastids are of several types, such as, chloroplast, leucoplast, chromoplast and so on. Plastids arise from smaller particles, the proplastids, found in the egg cytoplasm. Plastids - Different types of Plastids and their functions in ... - BYJUS Plastids are double-membrane organelles which are found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are responsible for manufacturing and storing of food. These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell. Explore More: Photosynthesis, Types of Plastids,
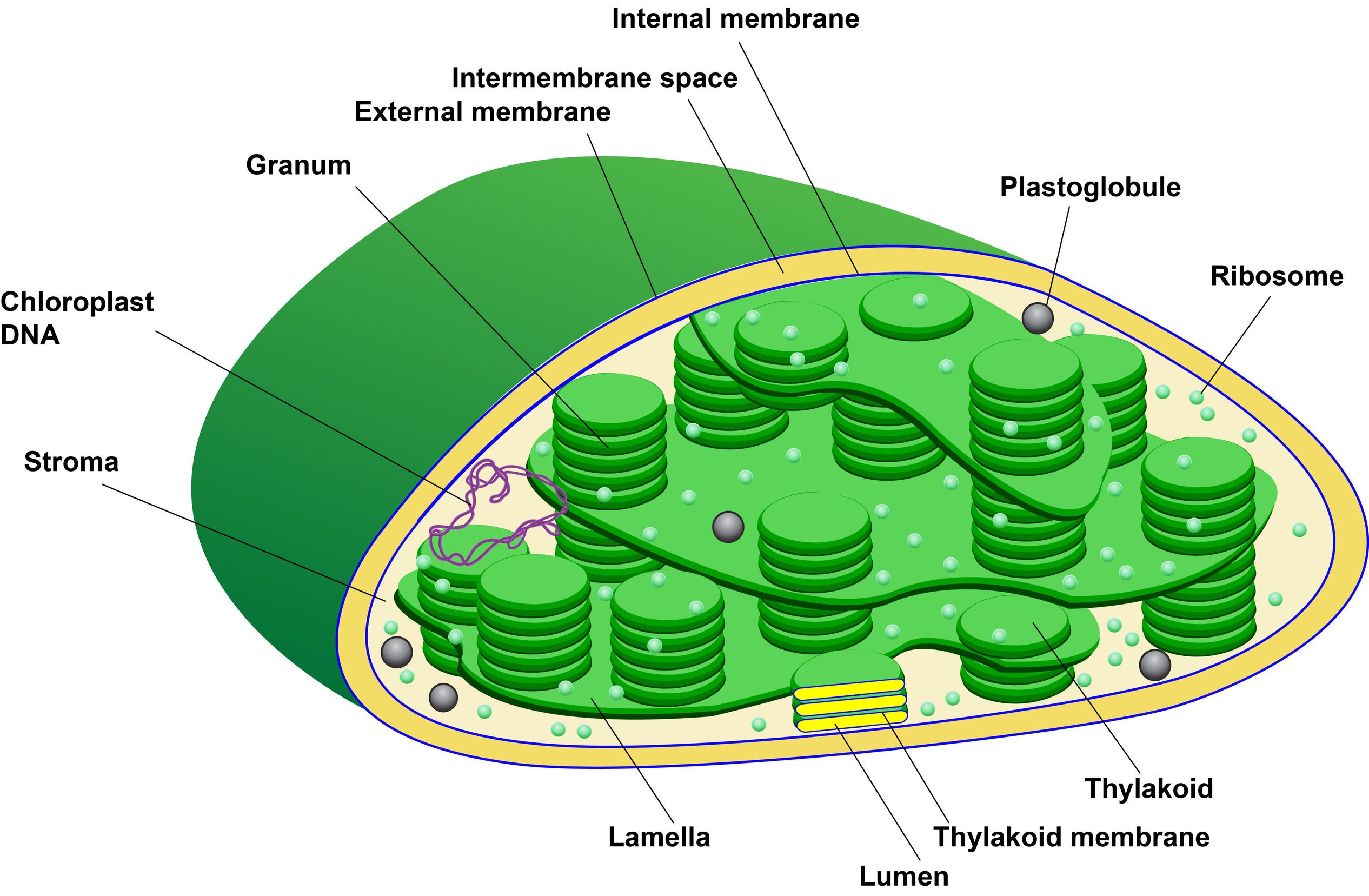
Plastids: Everything You Need to Know and More Plastids are a diverse group of double-membrane bound organelles found in most plants and algae. They may also be found in ferns, moss, parasitic worms and marine mollusks. Apart from photosynthesis, these organelles also assist in food storage and synthesis of compounds such as lipids, amino acids and carbohydrates. chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location, & Diagram chloroplast, structure within the cells of plants and green algae that is the site of photosynthesis, the process by which light energy is converted to chemical energy, resulting in the production of oxygen and energy-rich organic compounds. Photosynthetic cyanobacteria are free-living close relatives of chloroplasts; endosymbiotic theory posits that chloroplasts and mitochondria (energy ... What is Plant cell? Introduction, Structure, and ... - BiokiMicroki Introduction -. Plants are multicellular organisms and their cells are eukaryotic. Like animal cells, the plant cells have membrane bound organelles and a nucleus. However, the plant cell differs from animal cells in many aspects. The plant cells have some special organelles that allows the cells to carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplast - Wikipedia A chloroplast / ˈ k l ɔːr ə ˌ p l æ s t,-p l ɑː s t / is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells.The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells.
Chloroplast Structure and Function in detail with Labelled Diagram The chloroplasts are the cell organelles which consist of these pigments. The 3 types of pigments present in plants are chlorophyll, carotenoids, and anthocyanins. Chlorophyll imparts the green color to plants. Plastids are membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelles that can be found in the cells of plants and algae. The Structure of Plastids | Chloroplast Structure and Function - Pinterest Jan 20, 2021 - Structure of plastids are explained with the help of diagram... Chloroplast structure and function are described in detail as an example of plastid. Plant Cell Diagram Pdf - A Labeled Diagram of the Plant Cell and ... Labeled diagram of plant cell, created with biorender.com. In a plant cell, chloroplasts are the most prominent forms of plastids that contain chlorophyll, the green pigment. Identify the cell structures that the red arrow is pointing to in the images of a plant cell diagram. Cell parts blank diagram wiring services today printable plant. Labeled Plant Cell With Diagrams | Science Trends The difference between plastids and pigments is that plastids contain the pigment as well as other structures like starches and fats. The chloroplast is the plastid, while the chlorophyll is the pigment. Chloroplasts have their own genes within them, much like mitochondria in animal cells, and they are what convert solar energy into carbohydrates.
Plant Cell-Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Figure: Labeled diagram of a plant cell, created with biorender.com, The plant cell is comprised of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, as well as plastids, which are essential for photosynthesis and starch storage, and enormous vacuoles that control cell turgor pressure.
Structure of 3-oxoacyl-(acyl-carrier protein) synthase II ... May 01, 2008 · The amino-acid sequences of KAS I and KAS II share 38% identity and their functions are closely related, catalyzing the condensation of acyl-ACP with malonyl-ACP. In plastids, KAS I extends C 4 in the substrate to C 16 in six rounds of elongation, whereas KAS II carries out an additional step to give a C 18 product (Olsen et al., 2001 ).
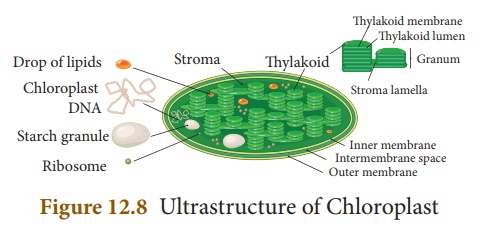
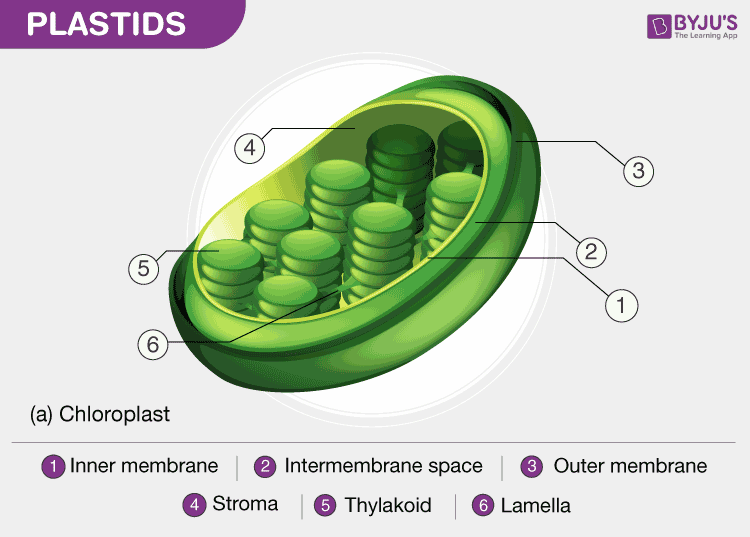
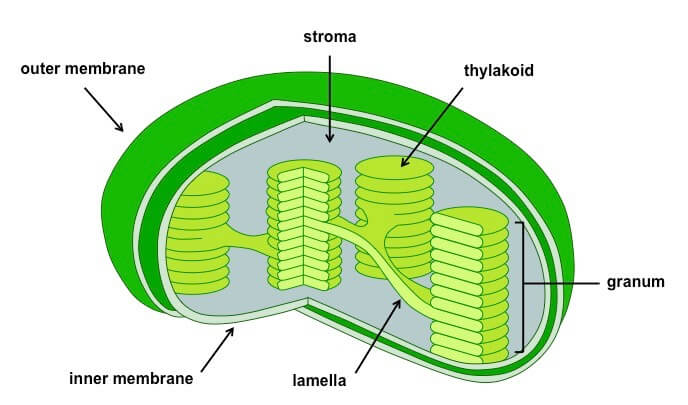
Plastids - Definition, Types, Main Structure and Function Studies have also shown the plastid to be polarized and ranging from 5 to 10 micrometers in width depending on the plant. Like the other plastids, chloroplasts have a double membrane envelope consisting of the outer and inner membrane (phospholipid layers). The space within the double membranes is covered with an aqueous matrix known as stroma.
Nelson Biology 12.pdf [30j71j2z320w] - doku.pub (a) Define osmosis and diffusion. (b) Make a sketch to represent each process in (a). Label your sketch. (c) Explain why these processes are essential for cellular function. K/U C 15. Draw a diagram to explain what happens to a cell in each of the following types of solutions. K/U C (a) isotonic (b) hypotonic (c) hypertonic Skills Review 16.
Biology Laboratory Manual 12th Edition [12 ed ... Figure 3.1 The size of cells and their contents. This diagram shows the size of human skin cells, organelles, and molecules. In general, the diameter of a human skin cell is about 20 micrometers (µm), of a mitochondrion is 2 µm, of a ribosome is 20 nanometers (nm), of a protein molecule is 2 nm, and of an atom is 0.2 nm.
Plastids- Definition, Structure, Types, Functions and Diagram Plastids Definition, Plastid is a double membrane-bound organelle involved in the synthesis and storage of food, commonly found within the cells of photosynthetic plants. Plastids were discovered and named by Ernst Haeckel, but A. F. W. Schimper was the first to provide a clear definition.
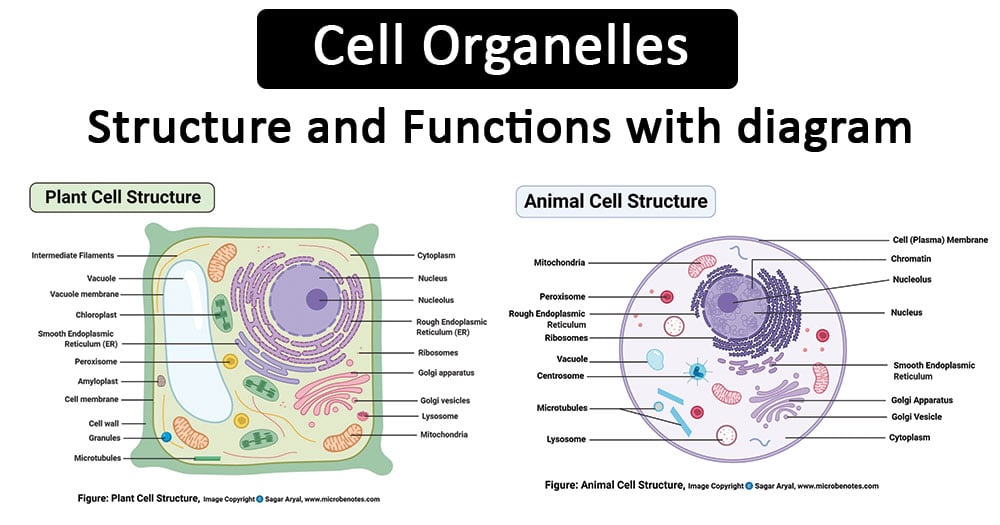
Plant Cell Diagram | Science Trends A plant cell diagram, like the one above, shows each part of the plant cell including the chloroplast, cell wall, plasma membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, etc. A plant cell diagram is a great way to learn the different components of the cell for your upcoming exam. Plants are able to do something animals can't: photosynthesize.
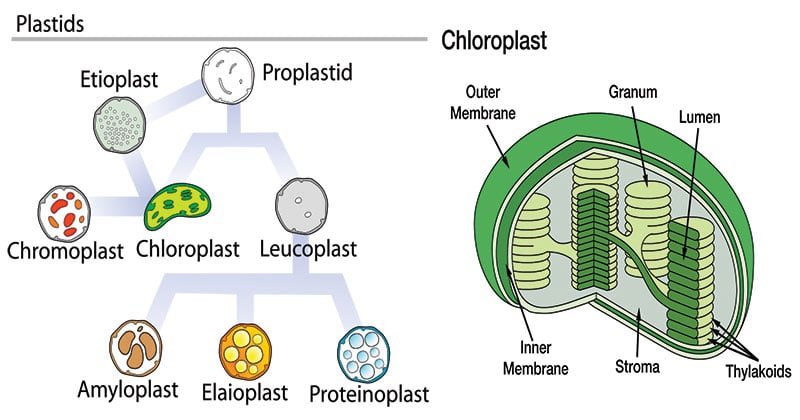
Plastids of Eukaryotic Cells: Types, Structure and Function (i) Leucoplasts- Colourless plastids, (ii) Chromoplasts - Coloured plastids (other than green) (iii) Chloroplasts- Green plastids, All the three types of plastids can change one form into another. Further, all plastids have a common precursor called pro-plastid. The pro-plastids are colourless undifferentiated plastids found in meristematic cells.
Animal Cells: Labelled Diagram, Definitions, and Structure - Research Tweet Animal Cells Organelles and Functions. A double layer that supports and protects the cell. Allows materials in and out. The control center of the cell. Nucleus contains majority of cell's the DNA. Popularly known as the "Powerhouse". Breaks down food to produce energy in the form of ATP.
Free Printable Plant and Animal Cells Worksheets Jun 27, 2022 · Animal Cell Diagram. Worksheets of animal cell diagrams help your students to visually see what the animal cell looks like and identify visually the parts that make up the animal cell. Blank, Labeled, and Coloring Animal Cell Diagram – Grab these three free diagrams. One is labeled for studying and reference, the second is labeled but needs ...
Types of Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Functions, Labeled Diagram Phloem cells. Meristematic cells. Epidermal cells. As described above, plant cells originate from the tip of the plant roots. The development of other cells is facilitated by the initial multiplication that takes at the tip, from the undifferentiated meristematic cells to form other specialized cells and cell tissues. 1.
History of botany - Wikipedia Botany (Greek Βοτάνη - grass, fodder; Medieval Latin botanicus – herb, plant) and zoology are, historically, the core disciplines of biology whose history is closely associated with the natural sciences chemistry, physics and geology.
Plastid - Wikipedia Plastid. Plant cells with visible chloroplasts. The plastid (Greek: πλαστός; plastós: formed, molded - plural plastids) is a membrane-bound organelle [1] found in the cells of plants, algae, and some other eukaryotic organisms. They are considered to be intracellular endosymbiotic cyanobacteria. Examples include chloroplasts (used for ...
Plant Cell: Definition, Structure, Function, Diagram & Types - Collegedunia Plant cell is a basic unit of a plant which consists of various cell organelles. Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that have a true nucleus with specialized structures, known as organelles, which carry out distinct functions. The main difference between a plant cell and an animal cell is the presence of a cell wall, cell membrane and chloroplast.
Plastids - Leucoplasts, Chromoplasts and Chloroplasts. - Biology Exams 4 U Plastids are the paint box where pigments are localized. These pigments will colour the different parts of the plant. Plastid is a general term that refers to a family of double membrane bound cytoplasmic organelles found in the plant cells and in some protists.
Plant Cell- Definition, Structure, Parts, Functions, Labeled Diagram Figure: Labeled diagram of plant cell, created with biorender.com, The typical characteristics that define the plant cell include cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin, plastids which play a major role in photosynthesis and storage of starch, large vacuoles responsible for regulating the cell turgor pressure.
Plastids: Definition, Diagram, Types, and Plastid Function - Embibe Plastids are remnants of a photosynthetic organism that was engulfed by the host, although not all are now photosynthetic. Plastid genomes encode genes for rRNAs, tRNAs and between about 28 and 150 proteins. Plastids can be categorized into 4 main groups: chloroplasts, cyanelles, apicoplasts and non-photosynthetic.
NOVEMBER 2018 LIFE SCIENCES P1 - Maths 101 2.2.1 Provide labels for 1 and 2. (2) 2.2.2 Give the number of the tissue that: (a) Gives rise to side/lateral roots (1) (b) Transports organic food in the plant (1) (c) Stores starch in the root (1) (d) Transports water in the plant (1) 2.2.3 Give ONE way in which the root hair is structurally adapted for its function. (2)
Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast - BYJUS The chloroplast diagram below represents the chloroplast structure mentioning the different parts of the chloroplast. The parts of a chloroplast such as the inner membrane, outer membrane, intermembrane space, thylakoid membrane, stroma and lamella can be clearly marked out. Chloroplast Diagram representing Chloroplast Structure,
Plant Cell: Diagram, Types and Functions - Embibe Exams Plastids in Plant Cell, They are membrane-bound organelles that have their own DNA. They are necessary to store starch, to carry out the process of photosynthesis. It is also used in the synthesis of many molecules, which form the building blocks of the cell. Based on the type of pigment, they are of Plastids are of three types: a.
Animal Cells Label The Organelles In The Diagram Below : Plant and ... They include the cell wall, large central vacuole, and plastids 19. As observed in the labeled animal cell diagram, the cell membrane forms the confining factor of the cell, that is it envelopes the cell ribosomes are small, spherical organelles comprising 65% ribosomal rna and 35% ribosomal proteins. Organelles in an animal cell.
























Post a Comment for "41 plastids diagram with labels"